MCP开发原理
1. MCP Server开发
1.1. 注意事项
- 使用stdio作为transport layer的时候,不要进行任何控制台输出
1.2. 交互过程
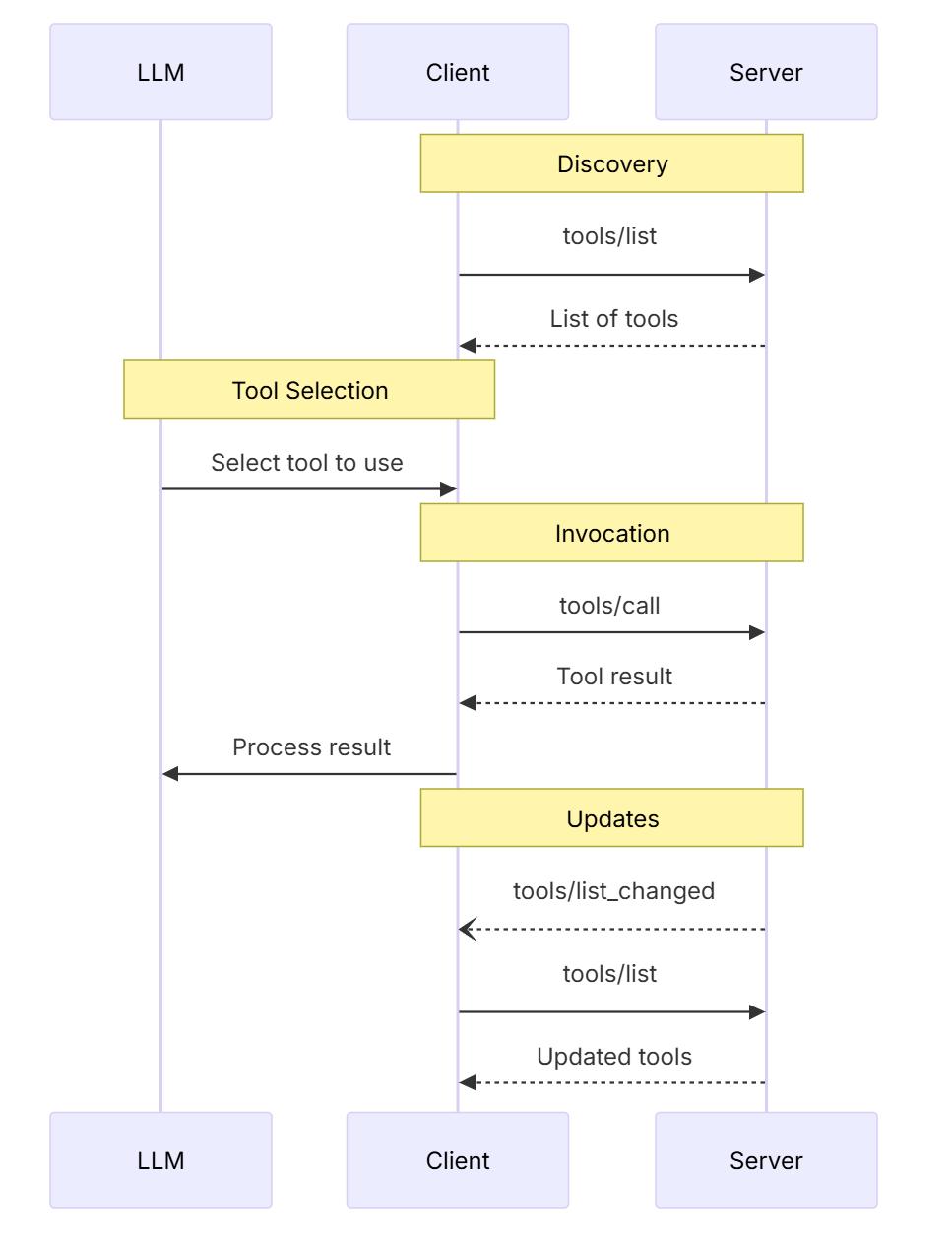
INITIALIZE = "initialize"
- 协商协议版本
- primitives支持情况,如tools、resources、prompts等features
- 是否支持notifications
LIST_TOOLS = "tools/list"
- 用于获取可用工具的列表
- 客户端调用此方法来发现服务端提供了哪些工具
- 返回工具的名称、描述、参数定义等元数据信息
CALL_TOOL = "tools/call"
- 执行具体的工具调用
- 客户端通过此方法调用特定工具,传递必要的参数
- 服务端执行工具逻辑并返回结果
PING = "ping"
- 连接保活和健康检查
- 用于测试连接是否正常,服务端是否响应
- 通常返回简单的确认消息
这些方法构成了MCP协议的基础通信框架,使得AI模型能够动态发现和调用外部工具,实现功能扩展。典型的交互流程是:初始化 → 列出工具 → 调用工具,期间穿插ping检查连接状态,更多信息可以参考https://modelcontextprotocol.io/docs/learn/architecture
1.3. 标准错误码
enum ErrorCode {
// Standard JSON-RPC error codes
ParseError = -32700,
InvalidRequest = -32600,
MethodNotFound = -32601,
InvalidParams = -32602,
InternalError = -32603,
}
SDKs and applications can define their own error codes above -32000.
1.4. tools发现
tool/list的响应需要包含以下关键部分
name: A unique identifier for the tool within the server’s namespace. This serves as the primary key for tool execution and should be URI-like for better namespacing (e.g.,com.example.calculator/arithmeticrather than justcalculate)title: A human-readable display name for the tool that clients can show to usersdescription: Detailed explanation of what the tool does and when to use itinputSchema: A JSON Schema that defines the expected input parameters, enabling type validation and providing clear documentation about required and optional parameters
AI应用从所有已连接的MCP服务器中获取可用工具,并将它们整合到一个统一的工具注册表中,供语言模型访问。这使得大语言模型(LLM)能够了解自己可以执行哪些操作,并在对话过程中自动生成相应的工具调用指令。
# Pseudo-code using MCP Python SDK patterns
available_tools = []
for session in app.mcp_server_sessions():
tools_response = await session.list_tools()
available_tools.extend(tools_response.tools)
conversation.register_available_tools(available_tools)
1.5. [官方weather示例](https://modelcontextprotocol.io/quickstart/server#windows)
1.5.1. 辅助函数
- 调用天气API接口
- 格式化alert输出
async def make_nws_request(url: str) -> dict[str, Any] | None:
"""Make a request to the NWS API with proper error handling."""
headers = {
"User-Agent": USER_AGENT,
"Accept": "application/geo+json"
}
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
try:
response = await client.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=30.0)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except Exception:
return None
def format_alert(feature: dict) -> str:
"""Format an alert feature into a readable string."""
props = feature["properties"]
return f"""
Event: {props.get('event', 'Unknown')}
Area: {props.get('areaDesc', 'Unknown')}
Severity: {props.get('severity', 'Unknown')}
Description: {props.get('description', 'No description available')}
Instructions: {props.get('instruction', 'No specific instructions provided')}
"""
1.5.2. tools实现
@mcp.tool()
async def get_alerts(state: str) -> str:
"""Get weather alerts for a US state.
Args:
state: Two-letter US state code (e.g. CA, NY)
"""
url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/alerts/active/area/{state}"
data = await make_nws_request(url)
if not data or "features" not in data:
return "Unable to fetch alerts or no alerts found."
if not data["features"]:
return "No active alerts for this state."
alerts = [format_alert(feature) for feature in data["features"]]
return "\n---\n".join(alerts)
@mcp.tool()
async def get_forecast(latitude: float, longitude: float) -> str:
"""Get weather forecast for a location.
Args:
latitude: Latitude of the location
longitude: Longitude of the location
"""
# First get the forecast grid endpoint
points_url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/points/{latitude},{longitude}"
points_data = await make_nws_request(points_url)
if not points_data:
return "Unable to fetch forecast data for this location."
# Get the forecast URL from the points response
forecast_url = points_data["properties"]["forecast"]
forecast_data = await make_nws_request(forecast_url)
if not forecast_data:
return "Unable to fetch detailed forecast."
# Format the periods into a readable forecast
periods = forecast_data["properties"]["periods"]
forecasts = []
for period in periods[:5]: # Only show next 5 periods
forecast = f"""
{period['name']}:
Temperature: {period['temperature']}°{period['temperatureUnit']}
Wind: {period['windSpeed']} {period['windDirection']}
Forecast: {period['detailedForecast']}
"""
forecasts.append(forecast)
return "\n---\n".join(forecasts)
1.5.3. mcp配置
{
"mcpServers": {
"weather": {
"command": "uv",
"args": [
"--directory",
"D:\\workspace\\proj\\weather",
"run",
"weather.py"
]
}
}
}
1.6. 交互过程
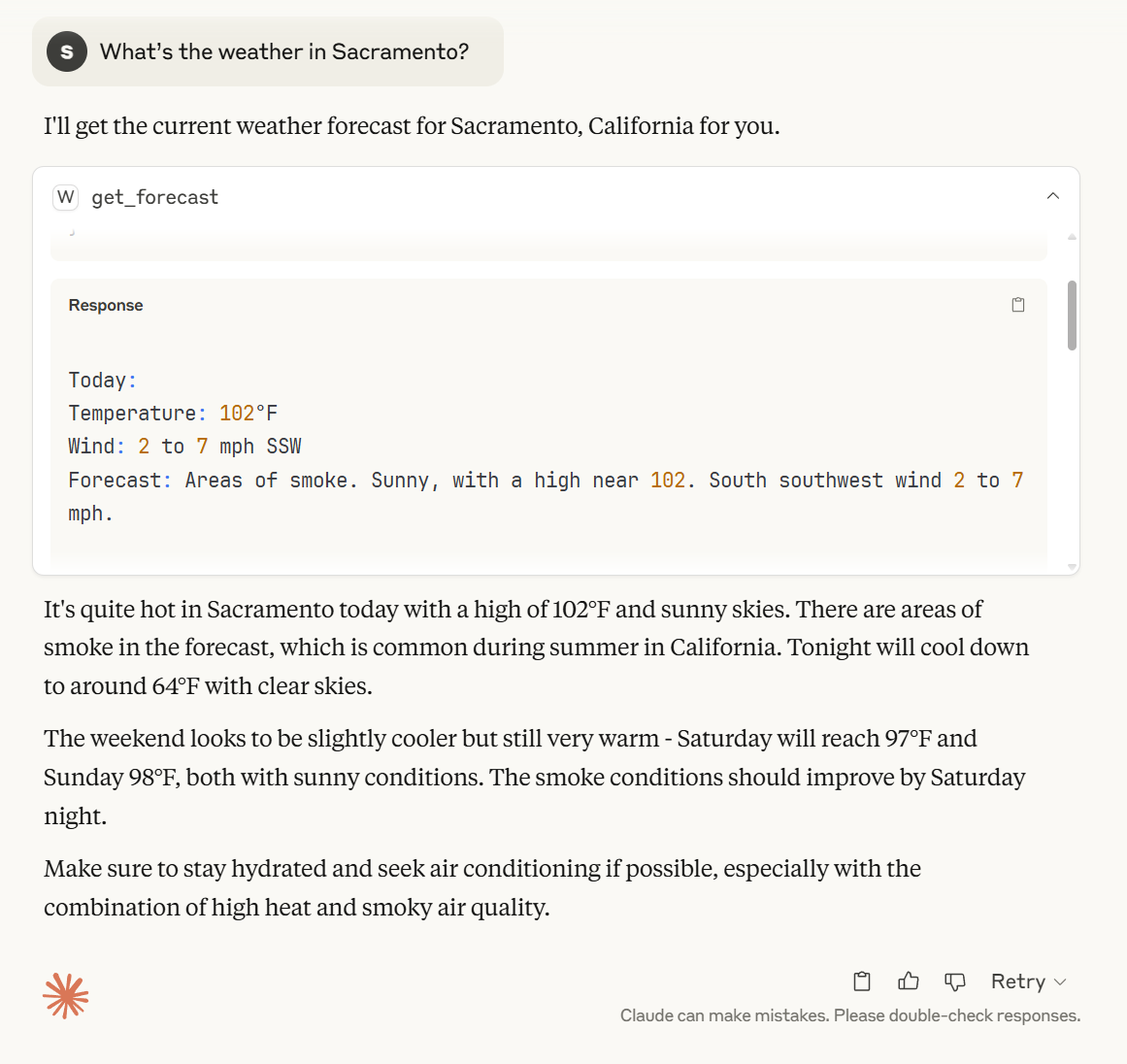
- The client(Claude desktop) sends your question to Claude
- Claude analyzes the available tools and decides which one(s) to use
- The client executes the chosen tool(s) through the MCP server
- The results are sent back to Claude
- Claude formulates a natural language response
- The response is displayed to you!
2. MCP Client开发
2.1. 官网client示例
2.2. 交互过程
- The client gets the list of available tools from the server
- Your query is sent to Claude along with tool descriptions
- Claude decides which tools (if any) to use
- The client executes any requested tool calls through the server
- Results are sent back to Claude
- Claude provides a natural language response
- The response is displayed to you