Mtls实现
1. 生成证书和密钥库
1.1. openssl配置
openssl中可以通过--config指定完整的配置文件,包含所有配置段(sections),用于生成包含扩展字段的证书签名请求(CSR)或自签名证书。
[req]
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name # 指定DN信息的配置段名
req_extensions = v3_req # 指定扩展字段的配置段名
prompt = no # 不提示用户输入,直接使用配置文件中的值
[req_distinguished_name]
C = CN # Country - 国家代码:中国
ST = Beijing # State/Province - 省/州:北京
L = Beijing # Locality - 城市:北京
O = shinerio # Organization - 组织名:shinerio
OU = IT Department # Organizational Unit - 部门:IT部门
CN = shinerio.site # Common Name - 通用名称:shinerio.site(主域名)
[v3_req]
# 密钥用途: # - digitalSignature: 数字签名(用于身份验证)
# - keyEncipherment: 密钥加密(用于加密对称密钥)
# - dataEncipherment: 数据加密(用于直接加密数据)
keyUsage = digitalSignature, keyEncipherment, dataEncipherment
# 扩展密钥用途: # - serverAuth: TLS/SSL服务器身份验证
extendedKeyUsage = serverAuth
# 主题备用名称:引用alt_names段的配置
subjectAltName = @alt_names
# 现代浏览器主要检查SAN
# Subject Alternative Name (SAN) 是X.509证书中的一个扩展字段,用于指定证书可以保护的额外域名、IP地址或其他标识符。CN只能指定一个主域名;SAN可以保护多个域名
[alt_names]
DNS.1 = shinerio.site
DNS.2 = web.shinerio.site
DNS.3 = localhost
DNS.4 = *.shinerio.site
IP.1 = 127.0.0.1
IP.2 = ::1
1.2. 生成客户端证书和服务端证书
# 生成CA密钥和证书
openssl genrsa -out ca.key 2048
openssl req -new -x509 -days 3650 -key ca.key -out ca.crt -subj "/CN=shinerio-CA"
# 生成服务器密钥和证书签名请求,指定server.conf文件,通过san指定了服务域名,否则浏览器会不信任域名。
openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048
openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr -config server.conf
# 使用CA签署服务器证书
openssl x509 -req -in server.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -out server.crt -days 3650 -extensions v3_req -extfile server.conf
# 创建服务器密钥库
openssl pkcs12 -export -in server.crt -inkey server.key -out server.p12 -name server -CAfile ca.crt -caname root -passout pass:changeit
keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore server.p12 -srcstoretype PKCS12 -destkeystore server.jks -deststoretype JKS -srcstorepass changeit -deststorepass changeit
# 创建服务器信任库,包含ca证书
keytool -import -alias ca -file ca.crt -keystore server_truststore.jks -storepass changeit
# 生成客户端密钥和证书签名请求
openssl genrsa -out client.key 2048
openssl req -new -key client.key -out client.csr -subj "/CN=Shinerio-Client"
# 使用CA签署客户端证书
openssl x509 -req -in client.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -out client.crt -days 3650
# 创建客户端密钥库,用于本地导入,实现客户端认证
openssl pkcs12 -export -in client.crt -inkey client.key -out client.p12 -name client -CAfile ca.crt -caname root -passout pass:changeit
keytool -importkeystore -srckeystore client.p12 -srcstoretype PKCS12 -destkeystore client.jks -deststoretype JKS -srcstorepass changeit -deststorepass changeit
# 创建客户端信任库,包含ca证书
keytool -import -alias ca -file ca.crt -keystore client_truststore.jks -storepass changeit
2. 本地安装ca证书和客户端证书
windows可以直接双击client.p12文件,导入到windows证书库中,浏览器访问指定网页时会弹框要求选择证书。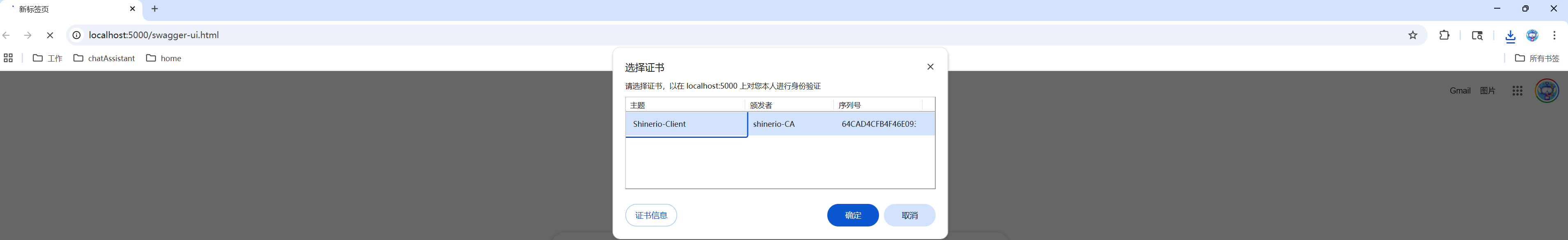
[!note]
在windows运行,建议使用git提供的/c/Program\ Files/Git/usr/bin/openssl.exe工具生成p12证书。 linux服务器下生成的p12文件可能无法被windows导入。
为了浏览器访问的时候,不提示风险,我们还需要把我们生成CA证书导入到系统受信任根证书颁发机构中。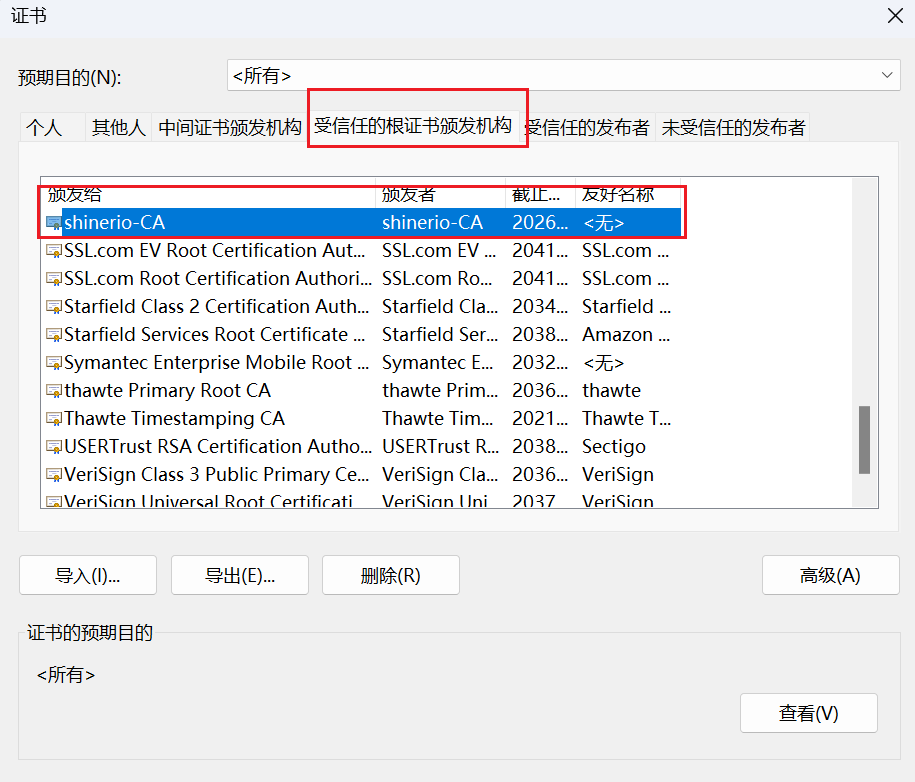
3. 客户端
// 加载客户端证书、私钥 KeyStore keyStore = loadKeyStore("client.jks", "changeit"); KeyStore trustStore = loadKeyStore("client_truststore.jks", "changeit");
// 创建KeyManagerFactory KeyManagerFactory kmf = KeyManagerFactory.getInstance(KeyManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm()); kmf.init(keyStore, "changeit".toCharArray());
// 创建TrustManagerFactory TrustManagerFactory tmf = TrustManagerFactory.getInstance(TrustManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm()); tmf.init(trustStore);
// 创建SSLContext SSLContext sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLS"); sslContext.init(
kmf.getKeyManagers(),
tmf.getTrustManagers(),
new SecureRandom() );
// 创建带有mTLS配置的HttpClient HttpClient client = HttpClient.newBuilder()
.sslContext(sslContext)
.sslParameters(createSSLParameters())
.build();
// 发送HTTP请求 HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create("https://localhost:8443/hello?name=Alice"))
.GET()
.build();
HttpResponse<String> response = client.send(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
// 打印响应 System.out.println("Status code: " + response.statusCode()); System.out.println("Response body: " + response.body());
核心在于sslContext.init方法,参数km用于像服务端发送自己的证书。
/** * Initializes this context. Either of the first two parameters * may be null in which case the installed security providers will * be searched for the highest priority implementation of the * appropriate factory. Likewise, the secure random parameter may * be null in which case the default implementation will be used. * * @param km the sources of authentication keys or null * @param tm the sources of peer authentication trust decisions or null * @param random the source of randomness for this generator or null */ public final void init(KeyManager[] km, TrustManager[] tm, SecureRandom random) throws KeyManagementException { contextSpi.engineInit(km, tm, random); }